

Then your password (or rather a token is used nowadays) would be stored in the Windows Credential Manager. $ git config -global core.excludesfile ~/. 111 Ideally, you should enter: git config -global credential.helper manager-core This is from the Microsoft multi-platform credential manager GCM. entire git config file (for example because you need to change just user.email. DS_Store files in your Git repositories, you can configure your Git to globally exclude those files: # specify a global exclusion list The gitconfig module changes git configuration by invoking git config. DS_Store (a hidden OS X system file that's put in folders) to your. On a Mac, it is important to remember to add. Third, Add your keys to GitHub by going into account settings. Please use a strong passphrase for your keys. # Enter file in which to save the key (/Users/you/.ssh/id_rsa): # Generating public/private rsa key pair. $ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C Creates a new ssh key, using the provided email as a label

The default settings are preferred, so when you're asked to "enter a file in which to save the key,"" just press enter to continue. Second, To generate a new SSH key, copy and paste the text below, making sure to substitute in your email. If you don't have either of those files go to step 2.

Open up your Terminal and type: $ cd ~/.sshĬheck the directory listing to see if you have files named either id_rsa.pub or id_dsa.pub. Most of the instructions below are referenced from here.įirst, we need to check for existing SSH keys on your computer. This might be difficult to configure in case you have two factor authentication enabled. So you don't have to type your username and password everytime, let's enable Git password caching as described here: $ git config -global credential.helper osxkeychain
#GIT CONFIG USERNAME CODE#
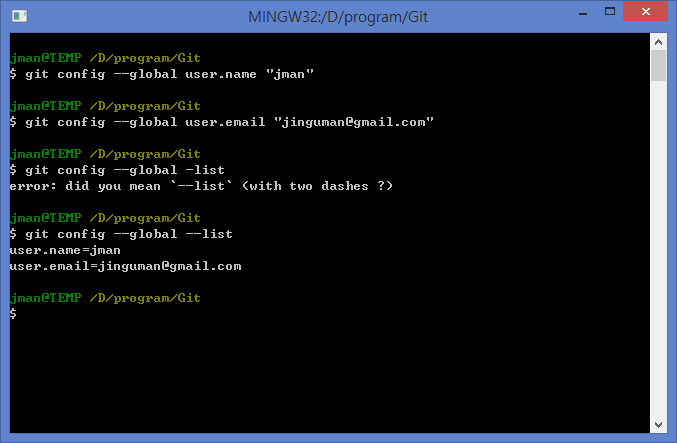
To push code to your GitHub repositories, we're going to use the recommended HTTPS method (versus SSH). $ git config -global user.email will get added to your. Next, we'll define your Git user (should be the same name and email you use for GitHub): $ git config -global user.name "Your Name Here" When done, to test that it installed fine you can run: $ git -versionĪnd $ which git should output /usr/local/bin/git.
#GIT CONFIG USERNAME INSTALL#
Git config -global user.What's a developer without Git? To install, simply run: $ brew install git While I’m in the Git username neighborhood, I’ll also add that you can view your Git email address with this command:Īnd you can change your Git email address like this: I just looked it up, and you should be able to change your Git username on a per-project basis like this, without the -global option: You can also have a different username on a per-project basis. I just did that on my test system, and it seems to work fine.Īgain, it’s important to note that this is your “global” username. Alexander"Īnother way to change it is to edit the Git config file in your HOME directory and change it there: You can change your Git username like this: You can also have a different username on a per-project basis (but I haven’t used that yet). It’s important to note that this is your “global” Git username. My file on my current test system looks like this: Here’s the git config command to show your Git username:Īnother way to show your Git username is with this git config command:įinally, you can also see your Git username in the Git configuration file in your HOME directory on Unix systems, i.e., this file: There are at least three ways to show your Git username:
#GIT CONFIG USERNAME HOW TO#
Git user FAQ: How do I show or change my Git username (or email address)? How to show your Git username


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
